50+ Essential Linux Commands: A Comprehensive Guide
- Nov 11, 2025
- 6 min read
50+ Essential Linux Commands: A Comprehensive Guide
Unlock the full potential of your Linux system with this comprehensive guide to essential Linux commands. Whether you’re a seasoned administrator or just starting out, mastering these commands is crucial for efficient server management, script writing, and troubleshooting. In this tutorial, you will learn the most frequently used and powerful commands for file management, process control, user access, network configuration, and system debugging.
You will learn over 50+ must-know Linux commands that will transform you into a Linux power user. From basic to advanced, these commands will become your go-to tools for tackling any task that comes your way.
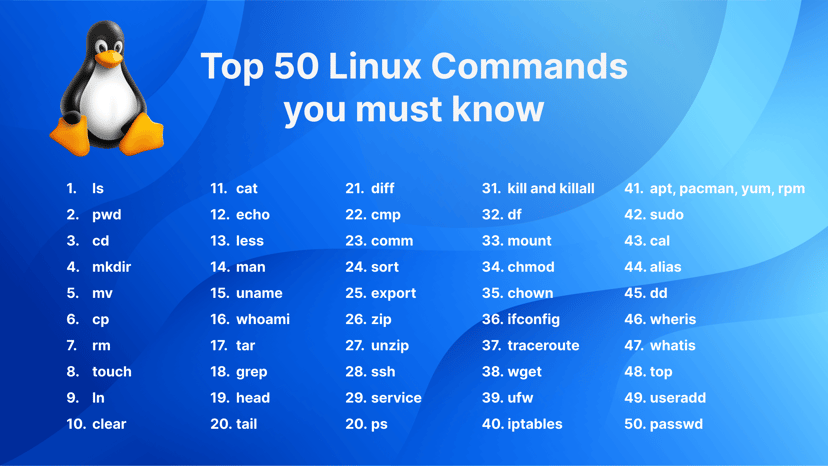
ls - The most frequently used command in Linux to list directories
less - Linux command to display paged outputs in the terminal
sort - Linux command to sort the content of a file while outputting
kill and killall - Kill active processes by process ID or name
traceroute - Trace all the network hops to reach the destination
iptables - Base firewall for all other firewall utilities to interface with
apt, pacman, yum, rpm - Package managers depending on the distribution
alias - Create custom shortcuts for your regularly used commands
whereis - Locate the binary, source, and manual pages for a command
useradd and usermod - Add a new user or change existing user data
Command | Description | Example |
ls | List directory contents. | ls |
cd | Change directory. | cd /path/to/directory |
pwd | Show current directory. | pwd |
mkdir | Create a new directory. | mkdir new_directory |
rmdir | Remove an empty directory. | rmdir empty_directory |
rm | Delete files or directories. | rm file.txt |
touch | Create an empty file. | touch new_file.txt |
cp | Copy files or directories. | cp file.txt /path/to/destination |
mv | Move or rename files. | mv file.txt /path/to/new_location |
cat | Display file contents. | cat file.txt |
nano / vim | Edit files in terminal. | nano file.txt |
find | Search for files in a directory hierarchy. | find . -name "file.txt" |
grep | Search text using patterns. | grep "pattern" file.txt |
tar | Archive and compress files. | tar -cvf archive.tar file1.txt file2.txt |
df | Show disk usage of file systems. | df |
du | Show directory/file size. | du -sh /path/to/directory |
chmod | Change file permissions. | chmod 755 file.txt |
chown | Change file owner. | chown user:group file.txt |
mount | Mount a filesystem. | mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt |
umount | Unmount a filesystem. | umount /mnt |
Command | Description | Sample Usage |
ping | Test connectivity to a host. | ping google.com |
ifconfig / ip a | Display network interfaces. | ifconfig or ip a |
netstat / ss | Show network connections. | netstat -tuln or ss -tuln |
wget | Download files via HTTP/FTP. | |
curl | Transfer data using URL syntax. | curl -O http://example.com/file.zip |
nc (Netcat) | Network debugging and data transfer. | nc -zv 192.168.1.1 80 |
tcpdump | Capture and analyze network packets. | tcpdump -i eth0 |
iptables | Configure firewall rules. | iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT |
traceroute | Trace the path packets take to a network host. | traceroute example.com |
nslookup | Query DNS to obtain domain name or IP address mapping. | nslookup example.com |
ssh | Securely connect to a remote host. | ssh user@example.com |
Command | Description | Example Command |
ps | Show running processes. | ps aux |
top | Dynamic process viewer. | top |
htop | Enhanced version of top. | htop |
kill | Send a signal to a process. | kill <PID> |
killall | Kill processes by name. | killall <process_name> |
uptime | System uptime and load. | uptime |
whoami | Current logged-in user. | whoami |
env | Display environment variables. | env |
strace | Trace system calls of a process. | strace -p <PID> |
systemctl | Manage systemd services. | systemctl status <service_name> |
journalctl | View system logs. | journalctl -xe |
free | Display memory usage. | free -h |
vmstat | Report virtual memory statistics. | vmstat 1 |
iostat | Report CPU and I/O statistics. | iostat |
lsof | List open files by processes. | lsof |
dmesg | Print kernel ring buffer messages. | dmesg |
Command | Description | Example Command |
passwd | Change user password. | passwd <username> |
adduser / useradd | Add a new user. | adduser <username> or useradd <username> |
deluser / userdel | Delete a user. | deluser <username> or userdel <username> |
usermod | Modify user account. | usermod -aG <group> <username> |
groups | Show group memberships. | groups <username> |
sudo | Execute commands as root. | sudo <command> |
chage | Change user password expiry information. | chage -l <username> |
id | Display user identity information. | id <username> |
newgrp | Log in to a new group. | newgrp <group> |
Command | Description | Example Command |
scp | Securely copy files over SSH. | scp user@remote:/path/to/file /local/destination |
rsync | Efficiently sync files and directories. | rsync -avz /local/directory/ user@remote:/path/to/destination |
ftp | Transfer files using the File Transfer Protocol. | ftp ftp.example.com |
sftp | Securely transfer files using SSH File Transfer Protocol. | sftp user@remote:/path/to/file |
wget | Download files from the web. | |
curl | Transfer data from or to a server. | curl -O http://example.com/file.zip |
Command | Description | Example Command |
awk | Pattern scanning and processing. | awk '{print $1}' file.txt |
sed | Stream editor for filtering/modifying text. | sed 's/old/new/g' file.txt |
cut | Remove sections from lines of text. | cut -d':' -f1 /etc/passwd |
sort | Sort lines of text. | sort file.txt |
grep | Search for patterns in text. | grep 'pattern' file.txt |
wc | Count words, lines, and characters. | wc -l file.txt |
paste | Merge lines of files. | paste file1.txt file2.txt |
join | Join lines of two files on a common field. | join file1.txt file2.txt |
head | Output the first part of files. | head -n 10 file.txt |
tail | Output the last part of files. | tail -n 10 file.txt |
Command | Description | Example Command |
alias | Create shortcuts for commands. | alias ll='ls -la' |
unalias | Remove an alias. | unalias ll |
history | Show previously entered commands. | history |
clear | Clear the terminal screen. | clear |
reboot | Reboot the system. | reboot |
shutdown | Power off the system. | shutdown now |
date | Display or set the system date and time. | date |
echo | Display a line of text. | echo "Hello, World!" |
sleep | Delay for a specified amount of time. | sleep 5 |
time | Measure the duration of command execution. | time ls |
watch | Execute a program periodically, showing output fullscreen. | watch -n 5 df -h |
Now let’s dive a little deeper into each of these commands and understand them in more detail. We already have a lot of existing articles for each of those individual commands. For your convenience, we’ll add links to all the existing articles, and continue to update the article as new topics are covered.
Command | Description | Example Command |
alias | Create shortcuts for commands. | alias ll='ls -la' |
unalias | Remove an alias. | unalias ll |
history | Show previously entered commands. | history |
clear | Clear the terminal screen. | clear |
reboot | Reboot the system. | reboot |
shutdown | Power off the system. | shutdown now |
date | Display or set the system date and time. | date |
echo | Display a line of text. | echo "Hello, World!" |
sleep | Delay for a specified amount of time. | sleep 5 |
time | Measure the duration of command execution. | time ls |
watch | Execute a program periodically, showing output fullscreen. | watch -n 5 df -h |
Now let’s dive a little deeper into each of these commands and understand them in more detail. We already have a lot of existing articles for each of those individual commands. For your convenience, we’ll add links to all the existing articles, and continue to update the article as new topics are covered.
The ls command is used to list files and directories in the current working directory. This is going to be one of the most frequently used Linux commands you must know of.
As you can see in the above image, using the command by itself without any arguments will give us an output with all the files and directories in the directory. The command offers a lot of flexibility in terms of displaying the data in the output.
Learn more about using the ls command
The pwd command allows you to print the current working directory on your terminal. It’s a very basic command and solves its purpose very well.
50+ Essential Linux Commands: A Comprehensive Guide
Author nerdcore pc systems





This paper offers a clear and insightful viewpoint. The emphasis on interactive digital services highlights how important they are becoming. More details are available on the website for those who like to learn more. It's always beneficial to hear such subjects handled objectively and factually.